Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a type of inflammatory arthritis that causes joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, and is often accompanied by the skin condition psoriasis. Doctors help patients identify the symptoms of psoriatic arthritis. Early diagnosis and management are key and there are many treatment options to alleviate discomfort and slow disease progression.
What is Psoriatic Arthritis?
Psoriatic arthritis is a type of arthritis that affects people who have psoriasis, a skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin. It is an autoimmune disease, which means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues, causing inflammation and damage.
Psoriatic arthritis can affect any joint in the body, but it most commonly affects the joints in the fingers, wrists, knees, toes and ankles. It can also cause inflammation in the spine, leading to pain and stiffness in the neck and lower back.
Symptoms of Psoriatic Arthritis
The symptoms of psoriatic arthritis can vary and change over time. Some common symptoms include:
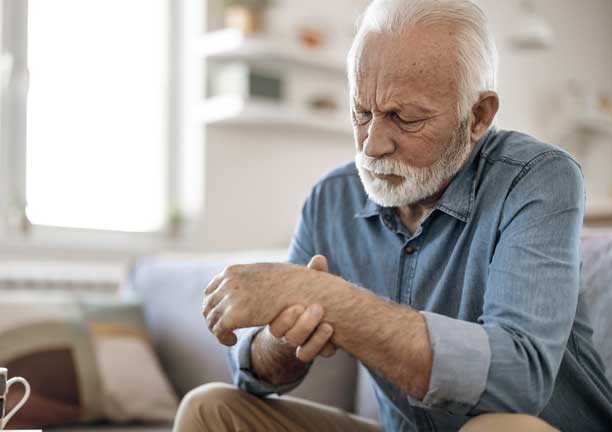
- Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling
- Redness and warmth in the affected joints
- Fatigue and sluggishness
- Nail changes
- Eye inflammation, which can cause redness, pain, and blurred vision
- Swelling of the fingers and toes
- Lower back pain and stiffness, which can be worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity
Not everyone with psoriatic arthritis will have all of these symptoms. Some people may experience mild joint pain, while others may have severe joint damage and disability.
Diagnosing Psoriatic Arthritis
Diagnosing psoriatic arthritis can be challenging, as its symptoms can be similar to other types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis. However, there are some key differences that can help doctors make an accurate diagnosis.
Firstly, psoriatic arthritis usually affects the joints on both sides of the body, while rheumatoid arthritis typically affects joints on one side of the body. Additionally, psoriatic arthritis often causes swelling in the fingers and toes, while rheumatoid arthritis does not.
To diagnose psoriatic arthritis, doctors will typically perform a physical exam, review the patient’s medical history, and order imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans. Blood tests may also be undertaken to check for inflammation and rule out other types of arthritis.
Treatments for Psoriatic Arthritis
While there is no cure for psoriatic arthritis, there are several treatment options available to help manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. The most common treatments include medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Medication for Psoriatic Arthritis
Medication is often the first line of treatment for psoriatic arthritis. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation, while disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can slow the progression of the disease and prevent joint damage.
In more severe cases, doctors may prescribe biologic drugs, which are genetically engineered proteins that target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation. These drugs can be administered through injections or infusions and have been effective in managing the symptoms of psoriatic arthritis.
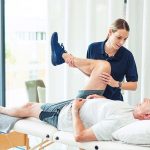
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is commonly prescribed for people with psoriatic arthritis. An exercise program to help improve joint mobility, reduce pain, and increase strength and flexibility will be customized for each patient. Therapists may also recommend assistive devices, such as braces or splints, to help support and protect affected joints.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage psoriatic arthritis symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on the joints, while a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce inflammation in the body.
Regular exercise is recommended for people with psoriatic arthritis. Low-impact activities, such as yoga, swimming, and cycling, can help improve joint mobility and reduce pain. Be sure to consult with your doctor or physical therapist before starting any new exercise routine.
Diagnosis and Management of Psoriatic Arthritis
Early diagnosis and management of psoriatic arthritis are crucial for preventing joint damage and disability. If left untreated, psoriatic arthritis can lead to permanent joint damage, which can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Additionally, people with psoriatic arthritis are at an increased risk of developing other health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and depression. By managing the disease early on, these risks can be reduced.
If you are experiencing joint pain or other symptoms similar to those described above, be sure to get a doctor’s evaluation. OrthoConnecticut’s orthopedic surgeons are adept at identifying and diagnosing psoriatic arthritis and help patients with individualized treatment plans to alleviate symptoms and help them lead active lives.